
#STEAM TABLE THERMODYNAMICS CALCULATOR FREE#
Table 4: IAPWS coefficients and exponents of equation 1.įor Region 2 the model is also based on Gibbs free energy g. Table 3: Derived from g used in equations of Table 1. Table 2: Thermodynamic relations related to Gibbs free energy g and the corresponding adimensional equations. 1, and can be obtained from the equations representing this region included in section 2.4.Īll the thermodynamic properties can be derived from equation 1 following the equations outlined in Tables 2 and 3. Where p s(T) represents the pressure at saturation, Region 4 in Fig. N i, I i, J i= IAPWS coefficients and exponents included in Table 4.Įquation 1 covers the following ranges of pressure and temperature in Region 1 as shown in Fig. The basic equation for Region 1 is an equation for the Gibbs free energy g, expressed in the adimensional form:
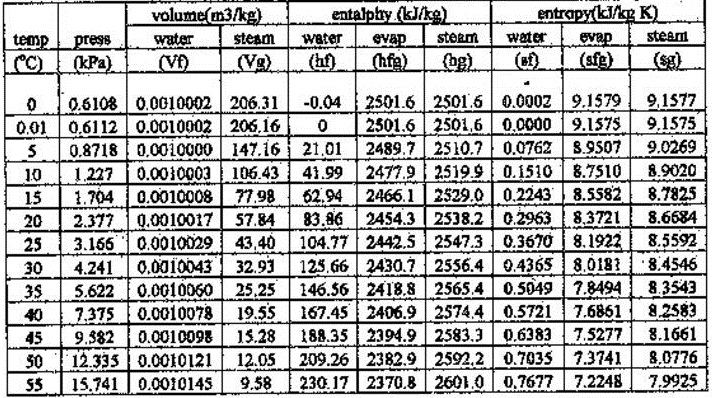
Table 1: Constants and properties of water Table 1 summarizes some of the constants and properties used in the model. Although the number of regions in the new model coincides with number in the previous model, some differences exist in the form in which the IFC-67 and IAPWS-IF97 models define the different regions. The IAPWS-IF97 model consists of a group of equations for a group of five graphical regions representing thermodynamic properties of water, and valid in the following ranges:įigure 1 shows the ranges within which the equations are valid, and the regions into which each range has been divided.
The new model was considered officially valid beginning in 1997, but due to the need for modifying existing design procedures and computational program codes, the IAPWS recommended an introductory period lasting at least until the end of 1999 during which IAPWS-IF97 was not officially mandated.
#STEAM TABLE THERMODYNAMICS CALCULATOR SERIES#
Each region requires the use of different equations, and furthermore the basic thermodynamic model chosen in relation to the interdependence of properties is not the same for each region.īased on these considerations, beginning in the decade of the 1980's, the International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam (IAPWS) decided to promote the development of a new series of investigations directed towards obtaining a new formulation for a model for the calculation of thermodynamic properties of water and steam, which was officially adopted in 1997 termed the "IAPWS Industrial Formulation 1997 for the Thermodynamic Properties of Water and Steam", subsequently known as IAPWS-IF97. It required division of the area of validity of its equations into five different regions due to the complexity of the behavior of the thermodynamic properties of water. The model was, however, was not easy to use. A great number of tables and diagrams existing in the literature, as well as computerized calculation programs were based on this model. Model IFC-67 was tested and recognized as reliable for the calculation of the thermodynamic properties of water. This model was developed from a variety of experimental data available for H 2O, which is the most abundant chemical compound in nature and also the most often used reagent in the chemical industry. In the decade of the 1960's a model was formulated for the calculation of thermodynamic properties of water for industrial use, and was known as the IFC-67 model. Keywords: thermodynamic properties, water and steam, calculation algorithms This paper presents the IAPWS-IF97 model in summarized form, and results obtained in applying it to the thermodynamic properties of water, including enthalpy, entropy, internal energy, and volume, in the states of compressed liquid, liquid-vapor equilibrium, and superheated steam, using calculation algorithms developed using common, universally available computational techniques. The new model is oriented toward facilitating calculations employing computers, improving accuracy, and improving consistency among the model's limiting regions as well as contributing towards improved process design and simulation. The latter model had been used for 30 years for the calculation of thermodynamic properties of water for industrial, scientific, and academic applications.

Was recommended before replacing the current model which had been developed in the 1960's (IFC-67). This new model, termed IAPWS-IF97, was adopted beginning in 1997, but an evaluation and changeover period 2ġDepartment of Chemical Engineering, Engineering Faculty, Universidad de Antofagasta, Antofagasta, Chile,ĢDepartment of Chemistry, Basic Sciences Faculty, Universidad de Antofagasta, Antofagasta, Chile,īeginning in 2000 the International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam (IAPWS) recommended the use of a new model for calculation of the thermodynamic properties of water and steam. Soc., 51, Nº 2 (2006), pags: 891-900ĬALCULATION OF THE THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF WATER USING THE IAPWS MODEL


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
